Ovarian Cancer Treatment in Bangalore, India
Cancer is a disease in which abnormal body cells proliferate rapidly. Even if cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it is usually named after the location of the body where it appears first.
Ovarian cancer is a group of diseases that develops in the ovaries and/or spread to the fallopian tubes and peritoneum. The peritoneum is the tissue lining that surrounds the abdominal organs.
Treatment is most effective in the early stages of ovarian cancer. It is critical to pay attention to your body and recognize any unusual indicators because ovarian cancer usually shows signs and symptoms. It is advisable to seek a physician’s consultation for accurate diagnosis and checkup.
Because of the complex nature of sub-types of ovarian cancer, you will need one of the best oncologist in India, like Dr. Sandeep Nayak, to conduct your treatment.
Dr. Sandeep Nayak is one of the best surgical oncologists in India. He is an expert in managing both routine and severe ovarian cancer cases and other malignancies like uterus cancer, stomach cancer, and so on.
If you are looking for the most-effective ovarian cancer treatment in India, this informative article can be a great help. Read on to know more.
What is ovarian cancer, and how does it affect you?
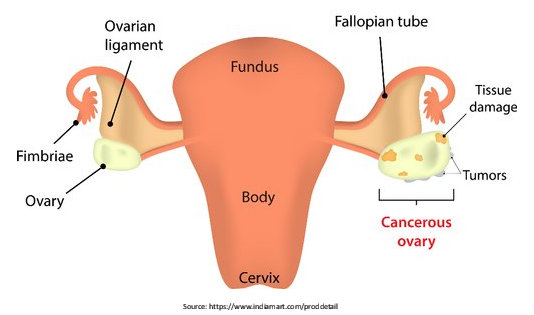
Ovarian cancer is the abnormal development of cells in the ovaries. The cells multiply and can penetrate and attack healthy body tissues.
Women have two ovaries on either side of the uterus in the pelvic region. Ovaries produce female hormones oestrogen and progesterone and also eggs for reproduction. There are two long and slender fallopian tubes on each side of the uterus which transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus.
Ovarian malignancies occur in several different tumour types. It is classified into four stages, frequently denoted by the Roman numbers I to IV. The earliest stage of cancer indicates that it is localized to the ovaries. By the fourth stage, cancer has spread to other body parts. High-grade serous carcinoma is the most widespread tumor type, accounting for almost 70% of all ovarian cancer cases.
What causes ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer can affect anyone with ovaries, including women, trans males, non-binary people, and intersex people. If your ovaries have been surgically removed, you cannot develop ovarian cancer.
You may have a higher chance of getting ovarian cancer if you:
- Inherit a defective gene, such as the BRCA genes or those linked to Lynch syndrome.
- Had either breast or bowel cancer.
- Had a prior malignancy that required radiotherapy.
- Have diabetes or endometriosis.
- Had periods at an early age.
- Had late menopause (over 55 years).
- Haven’t had a baby; this factor could indicate that you have discharged more eggs (ovulated more).
- Are taking hormonal therapy but have never used hormonal contraception such as the pill or an implant.
- Are obese or overweight.
- Are smoker.
Who is at risk for ovarian cancer?
The exact cause of ovarian cancer is unknown. However, the following factors can make you more vulnerable:
- Medical history of breast, uterine, or colon cancer.
- Mutations in genes linked to ovarian cancer, such as BRCA1 or BRCA2.
- Earlier experience of ovarian cancer.
- Overweight or obesity.
- Take reproductive medicines or hormonal therapy.
- No history of conception.
- Endometriosis.
- Another risk factor is advanced age. The majority of ovarian cancer cases occur after menopause.
Ovarian cancer can occur even if none of these risk factors are present. Similarly, possessing these risk factors does not guarantee that you will get ovarian cancer.
What are the signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer symptoms commonly include:
- Swollen abdomen or persistent bloating.
- Pain and stiffness in the stomach or the region between the hips.
- Loss of appetite or feeling full after having small meals.
- Urge or need to urinate frequently.
Ovarian cancer can also cause the following symptoms:
- Back pain
- Indigestion
- Constipation or diarrhoea
- Feeling exhausted
- Sudden weight loss
- Vaginal bleeding after the menopause
Diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer
 Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS):
Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS):
It is a sound-wave imaging diagnostic that detects tumours in the reproductive organs. However, TVUS cannot assist in determining whether tumours are malignant.
1. Imaging tests:
Tests such as ultrasound or CT scans of your abdomen and pelvic region can determine the size, shape, and structure of your ovaries.
2. Blood tests:
Your doctor may order a blood test for tumour markers that often indicate ovarian cancer. For example, a cancer antigen (CA) 125 test can identify a protein usually seen on the surface of ovarian cancer cells. These tests will not confirm cancer but provide information about the diagnosis and prognosis.
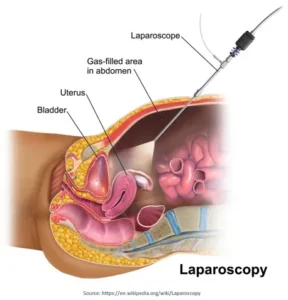
3. Laparoscopy:
The doctor will insert a thin tube having a camera (laparoscope) through a small hole in the abdomen to view the ovaries and maybe obtain a tissue sample for biopsy.
4. Biopsy:
A biopsy is a procedure that includes obtaining a tiny sample of tissue from the ovary and examining it under a microscope. Doctors may perform it as part of the initial examination or after surgical tumour removal. Only a biopsy can confirm whether or not a person has cancer.
Ovarian Cancer Treatment in Bangalore
- Ovarian cancer affects one in every 70 women at some point in their lives. Because there are no screening tests for ovarian cancer and the symptoms are often modest, most cases are diagnosed at an advanced stage.
- After confirming ovarian cancer diagnoses, the doctor will identify the stage of cancer-based on the results of your tests and procedures.
- Dr. Sandeep Nayak, a seasoned oncologist in Bangalore, may lead you through the whole treatment process. He will collaborate with you to provide you with the best possible ovarian cancer treatment in Bangalore, India.
- When offering recommendations, Dr. Nayak may develop a one-of-a-kind, individualized strategy for each patient, taking into account all health characteristics.
Ovarian cancer treatment depends on:
- The size and type of ovarian cancer.
- The location of the tumour.
- The severity of the disease.
- The general well-being of the patient.
The main ovarian cancer treatments are surgery and chemotherapy. Other options include targeted medicines and hormone therapy.
Surgery
One of the most significant aspects of ovarian cancer treatment is the quality of a patient’s surgery. Dr. Sandeep Nayak is one of the leading surgical oncologist in India. He is highly skilled in treating gynecologic cancers and offers the best surgical care.
- Patients may rest assured that they will receive the highest level of surgical treatment from Dr. Sandeep Nayak as he executes hundreds of oncology procedures each year.
- Surgery is the most common treatment for ovarian cancer. Our cancer specialist in Bangalore may advise surgery when there is the possibility of successful removal of the majority of the tumour or damaged tissue. Some early-stage ovarian cancer patients may be candidates for minimally invasive techniques to remove ovarian tumours and/or preserve fertility.
- Dr. Sandeep Nayak, a proficient surgical oncologist in Bangalore, is adept in a wide range of laparoscopic and robotic surgical techniques. These less-invasive procedures involve smaller incisions, promoting speedy and complete recovery.
Other surgical techniques for ovarian cancer include:
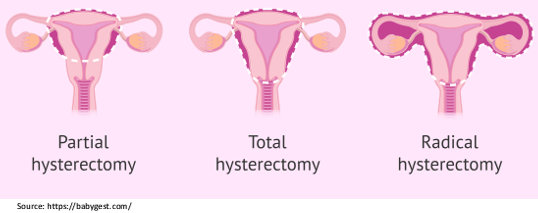
Hysterectomy
It involves removing the diseased uterus and the cervix.
Laparoscopic unilateral or bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy:
This minimally invasive surgical process entails removing affected ovaries or fallopian tubes. Generally, surgeons recommend this surgery to patients with no chance of preserving the ovary.
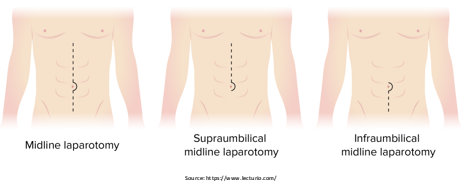
Laparotomy:
During this procedure, the surgeon creates an incision in the abdomen to remove malignant tissue and, if necessary, abdominal fluid.
Chemotherapy
It is the medication that destroys cancerous cells. Often, medical oncologists administer it before and after surgery or independently. It could potentially treat recurred ovarian cancer.
Radiotherapy
It uses high-energy rays of radiation to kill cancer cells. Radiotherapy for ovarian cancer may be used to:
- Treat advanced cancer if other treatments are ineffective.
- Relieve symptoms such as bleeding, pain, or discomfort.
Targeted therapy
It comprises drugs that solely attack cancer cells’ ability to grow and survive. They might be a good alternative if you have advanced ovarian cancer that has returned.
Hormone therapy
Certain ovarian cancers require oestrogen hormone to progress. Hormonal therapy can block oestrogen production to slow down the growth of some cancers.
During and after any treatments, you will undergo regular check-ups. Your doctor may also order some tests and scans to check the recurrence of the malignancy.
If you are concerned about any symptoms or side effects, speak with your doctor, don’t wait until your next appointment.
Prevention of Ovarian Cancer
There are no proven ways for lowering or preventing your risk of ovarian cancer. However, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk.
Factors that may reduce the risk of getting ovarian cancer include:
- Taking contraceptive pills.
- Pregnancy.
- Breastfeeding.
- Surgeries on reproductive organs like tubal ligation or hysterectomy.
What is the long-term outlook on ovarian cancer?
- If diagnosed early enough, all kinds of ovarian cancer can be treated. In the advanced stages, several types are also highly curable.
- When looking at ovarian cancer survival rates, it’s crucial to remember that medical advancements have improved the outlook in the last two decades.
- Nevertheless, regular monitoring and seeking aid if any symptoms develop can often lead to an early diagnosis and effective treatment.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What are the early warning signs of ovarian cancer?
Early warning signs of ovarian cancer include abdominal bloating, pelvic or abdominal pain, difficulty eating or feeling full quickly, and urinary urgency or frequency.
Is cancer in the ovaries curable?
The curability of ovarian cancer depends on factors like stage, type, and individual health. Early detection and treatment increase survival rates, but it’s challenging to guarantee a complete cure in advanced stages. Regular screenings and medical interventions are vital for managing the disease.

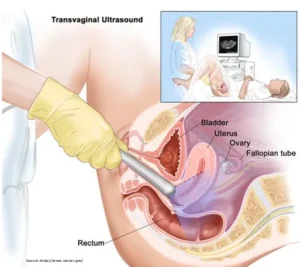 Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS):
Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS):