Prostate cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers among men, with over 1.4 million new cases globally each year. In India, prostate cancer rates have steadily increased, becoming one of the top diagnoses in male cancer patients. As men age, the risk of developing prostate cancer increases, with many cases detected at early stages. Stage 2 prostate cancer, or prostate cancer stage II, is considered localized, meaning it has not yet spread to distant parts of the body.
Dr. Sandeep Nayak, a highly regarded surgical oncologist in Bangalore, India, states, ” While prostate cancer can be concerning, stage 2 is often highly treatable, with several treatment options available that can lead to a successful outcome when diagnosed early.”
At MACS Clinic, Dr. Sandeep Nayak leads a team of specialists in providing comprehensive, personalized care for patients with prostate cancer. With years of experience in managing prostate cancer, Dr. Nayak’s expertise in the treatment of stage 2 prostate cancer ensures that patients receive the most effective, tailored solutions for their condition. From advanced diagnostics to state-of-the-art treatment options, Dr. Nayak offers the highest standard of care for patients diagnosed with prostate cancer stage II.
What is Stage 2 Prostate Cancer?
In stage 2 prostate cancer, the cancer is localized. It indicates that the cancer cells are confined to the prostate gland and have not metastasized. At this stage, the cancer would be much more aggressive than stage 1 prostate cancer, but it has not yet extended to either the lymph nodes and/or distant sites.
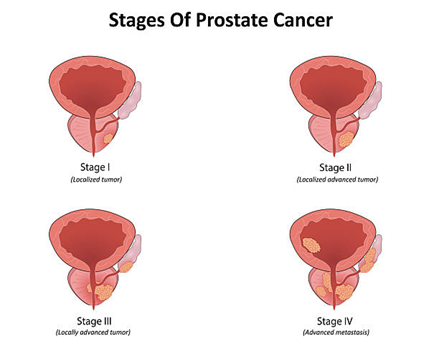
Stage II is divided into 2a and 2b based on tumor size and extent, with 2b possibly affecting one or both sides of the prostate. Often asymptomatic, many men may not notice symptoms, but it remains highly treatable with various medical interventions.
Causes and Risk Factors of Stage 2 Prostate Cancer
- Age: The risk increases significantly after age 50, with most cases occurring in men over 60.
- Family History: If there are relatives in the family having prostate cancer, particularly first-degree relatives such as father/brother, then risk increases.
- Race: African-American men are at a higher risk of developing prostate cancer compared to other racial groups.
- Genetics: Inherited gene mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, can elevate the risk of prostate cancer.
- Diet: Diets high in fat, particularly animal fats, may increase the risk of prostate cancer.
- Obesity: Overweight men have a higher risk of developing aggressive forms of prostate cancer.
- Hormones: Higher levels of testosterone may promote the growth of prostate cancer cells
- Environmental Factors: Certain chemicals and toxins could contribute towards the causative factors, although there is inadequate evidence.
Stage 2 Prostate Cancer Symptoms
- Asymptomatic: For most men with Stage 2 prostate cancer, symptoms may not be apparent.
- Urinary Symptoms: Some men may have problems with urination, such as difficulty urinating, frequent urination, and weak urination flow.
- Bloody Urine or Semen: Rare, but may occur in some cases.
Pelvic Pain: Generally, low discomfort or pain in the pelvic area may arise, which is quite rare in this period.
Erectile Dysfunction: Some men may feel the inability to generate or maintain an erection.
No Pain: The vast majority of the time, there is little or no pain with stage 2 prostate cancer.
Given that symptoms are minimal at this stage, screening and PSA testing are essential for early detection.
Diagnosis of Stage 2 Prostate Cancer
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE):
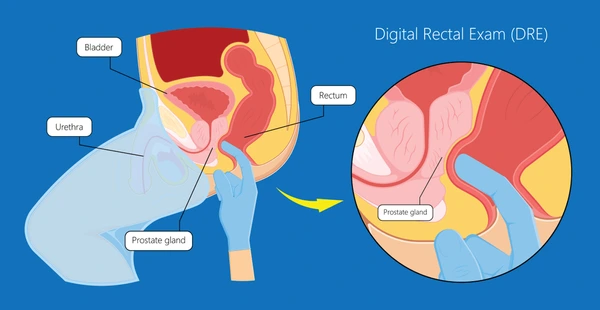
A physical examination in which a doctor feels the prostate for abnormalities or lumps.
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test:
A blood test is performed to determine PSA levels. A high level of PSA may suggest the possible existence of prostate cancer.
- Biopsy:
If cancer is suspected, a prostate biopsy is performed to confirm the presence of cancer cells by taking small tissue samples from the prostate.
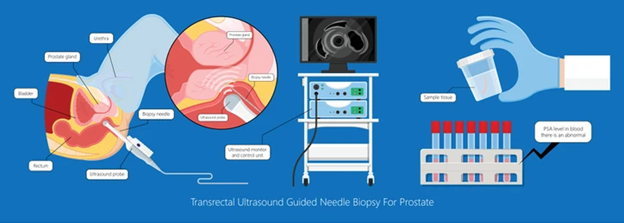
- Transrectal Ultrasound (TRUS):
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
- CT or Bone Scans:
Treatment Options for Stage 2 Prostate Cancer
Stage 2 prostate cancer is highly treatable, and the treatment approach will depend on various factors, including the tumor’s size, location, and the patient’s overall health. The primary treatment options for stage 2 prostate cancer include:
- Surgery (Radical Prostatectomy):
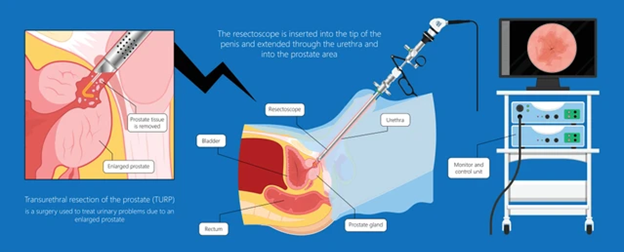
It entails the removal of the prostate gland and is the most widely used mode of treatment in cases of localized prostate cancer.
- Radiation Therapy:
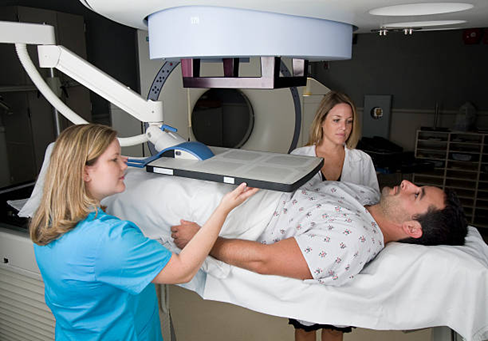
Radiation uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. This treatment may be administered externally or via an internal technique known as brachytherapy.
- Active Surveillance:
In some patients, especially those with low-risk cancer, the doctor might advise close monitoring in place of immediate treatment – active surveillance.
- Hormone Therapy:
Occasionally, one may use hormonal therapies to shrink a tumor before any other therapies are applied.
There are various treatments, each with its own benefits and risks, which will be determined in collaboration with your physician.
Stage 2 Prostate Cancer Survival Rate
The rate of survival in stage 2 prostate cancer is very high. In fact, the vast majority of patients achieve long-term remission. According to statistics, the 5-year survival rate in stage 2 prostate cancer approaches 100 percent, especially if it is localized.
The survival rate may depend on factors such as the patient’s age, overall health, and the effectiveness of the treatment. Stage 2 prostate cancer has one of the best survival rates among all the stages of prostate cancer.
Prognosis for Stage 2 Prostate Cancer
Stage 2 prostate cancer has a favorable prognosis and can easily be treated when found early and treated successfully. In most cases of prostate cancer that have reached stage 2, the man can survive for several years after treatment without a high risk of recurrence.
In some cases, patients may need to follow up periodically to monitor for cancer recurrence. It is based on the cancer’s aggressiveness, the patient’s age, and their overall health.
Side Effects of Treatment for Stage 2 Prostate Cancer
Treatment for stage 2 prostate cancer can lead to various side effects, depending on the type of treatment chosen. For example:
- Surgery (Radical Prostatectomy): Common side effects include erectile dysfunction, urinary incontinence, and changes in sexual function.
- Radiation Therapy: Side effects may include fatigue, urinary issues, and bowel discomfort.
- Hormone Therapy: Hot flashes, decreased libido, and fatigue are common side effects of hormone therapy.
Although such side effects may prove challenging, they are usually temporary and can be managed with medical care and lifestyle changes.
Life After Stage 2 Prostate Cancer Treatment

Life after completing treatment for stage 2 prostate cancer will be different for one man to another; many men are able to lead very active and complete lives after treatment. Following treatment is an integral part of making sure that the cancer does not come back; it is also necessary to take care of any problems that may come from treatment. Many men may still have some lasting side effects, such as changes in sexual function or urinary issues, which can be managed with rehabilitation and therapy.
Staying physically active, eating a balanced diet, and maintaining regular medical checkups are key to staying healthy after treatment.
Conclusion
Stage 2 prostate cancer is a highly treatable condition with a favorable prognosis when detected early and treated appropriately. With treatment options ranging from surgery and radiation to active surveillance, men diagnosed with stage 2 prostate cancer can achieve long-term survival and quality of life. Working closely with a competent specialist, such as Dr. Sandeep Nayak, to determine the best treatment plan is crucial for a positive outcome.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can stage 2 prostate cancer be cured?
2. What’s the difference between stage 1 and stage 2 prostate cancer?
3. How often should I get a PSA test after treatment?
4. Is radiation therapy effective for stage 2 prostate cancer?
5. What are the chances of prostate cancer coming back after treatment?
Reference links:
https://www.healthline.com/health/mens-health/stage-2-prostate-cancer
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/stage-2-prostate-cancer
Disclaimer: The information shared in this content is for educational purposes and not for promotional use.