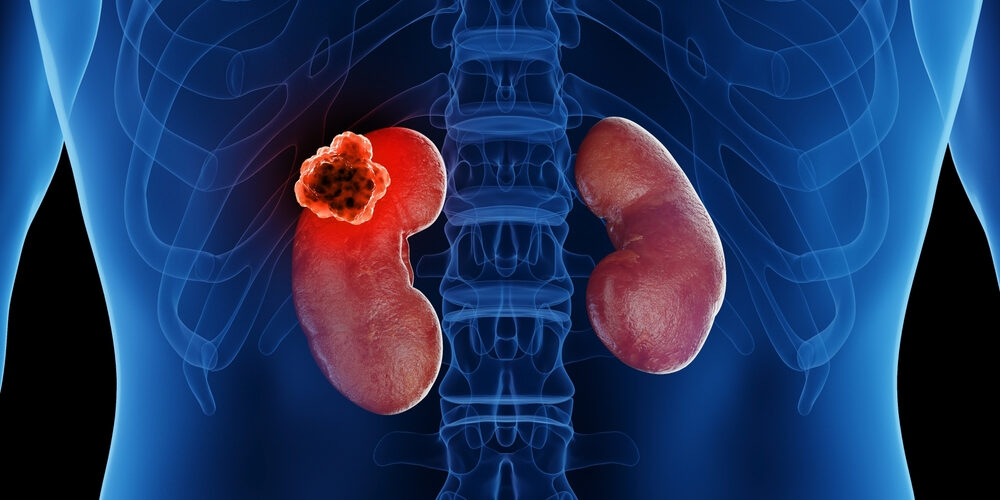
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a form of kidney cancer that begins in the lining of tiny tubes or tubules of the kidney. It accounts for approximately 2-3% of all adult malignancies globally.
- Annually, RCC sees about 137,000 cases in Europe, 76,000 in North America, and 403,000 globally.
- In 2022, 79,000 US patients were diagnosed with kidney cancer, leading to 13,920 deaths.
- Annual incidence of RCC among Indian males is reported at 2 per lakh population and females at 1 per lakh population accounting for 3% of all cancers.
- 15-20% of RCC come in stage 4 at the time of first diagnosis.
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma, also known as metastatic kidney cancer, is when the cancer spreads to other parts of the body. This is also called stage 4 cancer. This aggressive form of cancer can profoundly affect patients and their loved ones, taking a toll both physically and emotionally.
India has seen a rise in the incidence of various cancers over the years, including RCC. In these trying times, many turn to experts for guidance and care. Among them is Dr. Sandeep Nayak, a leading surgical oncologist in India. His in-depth knowledge of the condition provides hope and direction for metastatic kidney cancer patients.
According to Dr. Sandeep Nayak:
“Understanding Metastatic RCC is not just essential for those diagnosed but also their supporters and caregivers. Being alert to specific changes in our body can pave the way for early detection.”
Wondering what signs you should look out for? Read on to understand the tell-tale signals.
Symptoms Of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
RCC is most commonly found in individuals aged 50-70, with an average diagnosis age of 64. The common signs that you must be alert to include:
- Blood in the urine: A common sign of metastatic renal cell cancer.
- Unexplained weight loss: Losing weight without trying can be a symptom.
- Pain in the side or back: A persistent ache might signal this condition.
- Swelling in the legs and ankles: Often due to fluid buildup.
- Fatigue: Patients often feel unusually tired or weak.
- Shortness of breath: Caused when cancer spreads to the lungs.
- Bone pain: When the cancer affects the bones, pain is a frequent symptom.
- High calcium levels: This can lead to feeling thirsty or frequent urination.

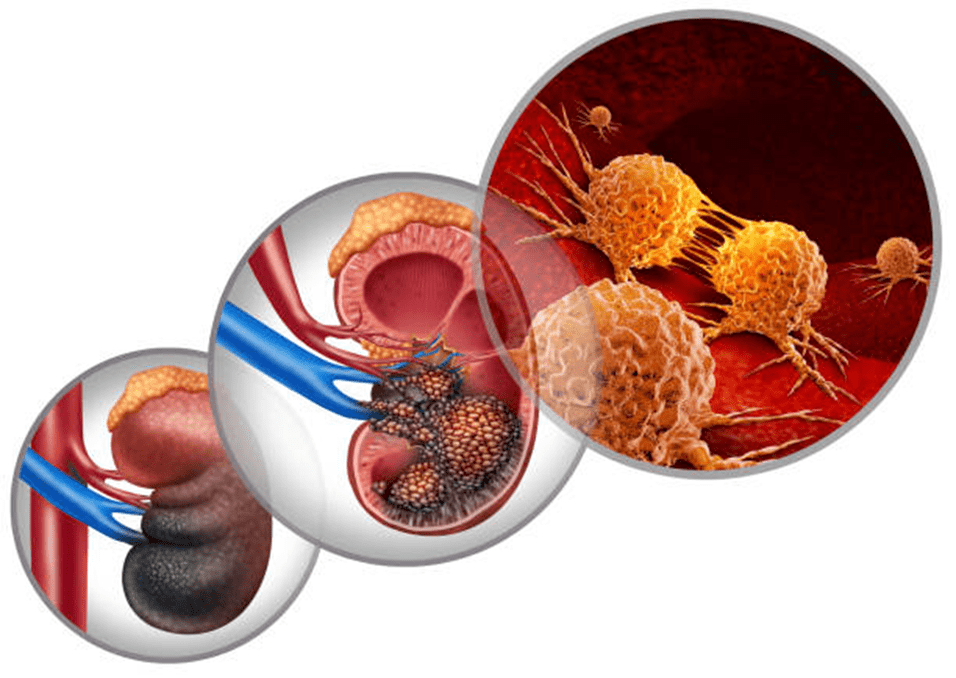
How Fast Does Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Grow?
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma can exhibit varying growth rates among patients. Some patients may experience slow progression over the years. While for others, the cancer might spread rapidly within months.
Several factors influence its progression, including:
- the subtype of RCC
- the patient’s overall health
- the effectiveness of treatments
- kidney cancer metastasis sites (the organs to which the cancer has spread)
What Are The Complications Of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma?
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) can lead to a variety of complications. This can occur both from the spread of the cancer itself and from the treatments used to manage it. Here are some potential complications of mRCC:
- Organ Dysfunction: As mRCC spreads to other organs, it can interfere with their normal function. For example, metastases to the lungs can lead to respiratory issues. If it spreads to the bones, it can result in fractures and pain.
- Lymphedema: This swelling can occur if mRCC blocks the lymphatic system, mainly if it spreads to lymph nodes.
- Hypercalcemia: Some people with mRCC develop elevated calcium levels in the blood, which can cause kidney stones, bone pain, and neuromuscular symptoms.
- Anemia: Reduced red blood cell count, leading to fatigue, shortness of breath, and other symptoms.
- Treatment-Related Side Effects: Targeted therapies and immunotherapies can lead to side effects, including fatigue, liver problems, skin reactions, and digestive issues.
- Pain: As tumors grow and spread, they can press against nerves or invade bones, causing significant pain.
- Kidney Dysfunction: The remaining kidney (after the doctor removes the affected one) may be impacted, leading to reduced kidney function.
- Brain and Neurological Issues: If mRCC spreads to the brain, it can lead to symptoms like seizures, headaches, and cognitive changes.
Please maintain regular check-ups and communicate any new or worsening symptoms to your healthcare provider. Early detection and management of these complications can improve the quality of life for individuals with mRCC.
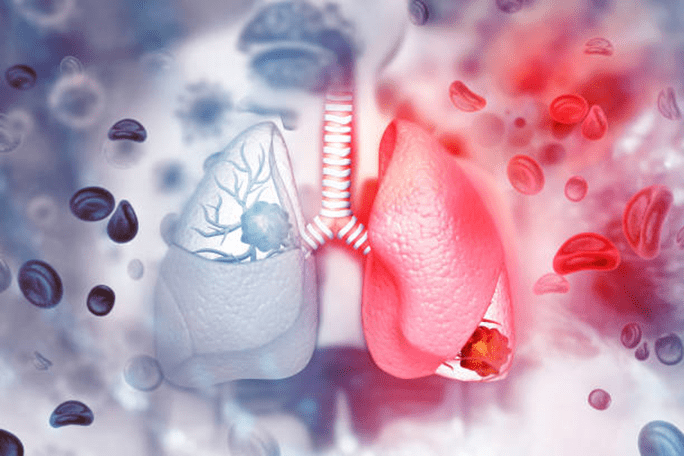
Most Common Site of Metastasis for Renal Cell Carcinoma
The lungs are the most frequent site of metastasis for renal cell carcinoma. It’s not uncommon for individuals initially diagnosed with metastatic renal carcinoma to discover it due to respiratory symptoms or findings on a chest X-ray.
Understanding where cancer spreads can be crucial in monitoring and early detection, something Dr. Sandeep Nayak often underscores in his consultations.
With over 15 years of cancer expertise, Dr. Nayak is the go-to doctor for kidney cancer treatment in Bangalore.
What Is The Survival Rate For Renal Cell Carcinoma Metastasis?
The metastatic renal cell carcinoma life expectancy can vary widely among patients. Numerous factors influence it:
Stage of the Disease: Life expectancy is generally shorter for those diagnosed at a more advanced stage.
Treatment Response: The effectiveness of metastatic renal cell carcinoma treatment for a particular individual can significantly impact their prognosis.
General Health and Age: A patient’s overall health, including the presence of other underlying conditions and their age, can play a role in life expectancy.
Sites of Metastasis: The organs or areas where the cancer has spread can affect prognosis. For instance, mRCC spreading to the brain or liver may have a different prognosis than when it spreads to the lungs or bones.
Performance Status: This measures how well an individual can perform ordinary tasks and daily activities. Those with a higher performance status often have a better prognosis.
Historically, the average life expectancy for mRCC was around 1 to 2 years. However, with new therapies, many patients are living longer, with some reaching beyond the 5-year mark.
What Is The Best Treatment For Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma?
The best treatment for metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) often depends on several factors, including:
- the patient’s overall health
- the specific subtype of RCC
- the extent and sites of metastasis
Over the years, there have been significant advancements in the treatment of mRCC. Here are some of the primary treatment modalities:
Targeted Therapies: These drugs specifically target the molecular differences between cancer and normal cells. Examples include sunitinib (Sutent), pazopanib (Votrient), and cabozantinib (Cabometyx), among others.
Immunotherapy: This treatment uses the body’s natural defenses to fight the cancer. Nivolumab (Opdivo), alone or in combination with ipilimumab (Yervoy), has been used for mRCC.
Cytokine Therapy: This is an older form of immunotherapy that includes drugs like interleukin-2 (IL-2) and interferon-alpha. They’re less commonly used today due to the development of newer, more effective treatments.
Radiation Therapy: While kidney cancer is often resistant to radiation, it may alleviate symptoms in specific metastatic sites, like bone metastases.
Surgery: In some instances, surgical removal of the primary kidney tumor and metastatic sites can be beneficial. cytoreductive nephrectomy is the term used when the diseased kidney is removed in stage 4 cancers. In patients with symptoms (for example, hematuria, pain, a large tumor thrombus, uncontrolled hypertension, or paraneoplastic symptoms), cytoreductive nephrectomy is still recommended for symptom relief.
In selected cases, it is possible to surgically remove the disease that has spread to lung or liver and attempt to cure stage 4 cancer. This may cure some of the patients with stage 4 kidney cancer.
Ablative Techniques: These are used less frequently but can be an option for specific patients. Techniques like cryoablation or radiofrequency ablation can destroy tumor cells.
Clinical Trials: For patients with mRCC that isn’t responding to standard treatments, participating in clinical trials can offer access to new and experimental therapies.
Patients must work closely with an oncologist to determine the most suitable treatment plan. Medical experts regularly employ a combination of treatments for optimal results.
Conclusion
Metastatic or stage 4 renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) is a complex medical condition requiring comprehensive understanding and tailored management. With advancements in medical research, promising metastatic RCC treatments are emerging, offering hope. However, the key to managing mRCC lies in early intervention, expert guidance, and a personalized treatment approach.
Cancer expert Dr. Sandeep Nayak, with his wealth of experience and dedication to patient care, stands as a beacon in this journey. If you or a loved one is grappling with mRCC, don’t navigate this path alone. Seek expert insights.
FAQs
Q.1 How long can you live after renal carcinoma?
A: Life expectancy after renal carcinoma varies based on factors like the stage at diagnosis and treatment received. However, with timely interventions, many individuals can live for years.
Q.2 What organs are affected by renal cell carcinoma?
A: Renal cell carcinoma originates in the kidneys, but it can spread to other organs. The lungs, bones, liver, and brain are common metastasis sites.
Q.3 Is Stage 4 renal cell carcinoma curable?
A: Stage 4 renal cell carcinoma is advanced and challenging to cure. However, metastatic RCC treatments can control its growth, manage symptoms, and extend life.
Q.4 How long can you live with stage 4 renal cell carcinoma?
A: The life expectancy for stage 4 renal cell carcinoma varies. With modern treatments, many patients can live for several years, though individual outcomes differ.