Do you or a loved one have concerns about breast cancer after menopause? You are not alone. According to statistics, 6 out of 10 breast cancer cases are detected in women who are 55 or older. This stresses that addressing the issues relevant to the post-menopausal years is essential.
In the blog, we’ll discuss menopause and breast cancer, its causes, treatments and more.
Keen to know the link between menopause and cancer risk? Let’s discover.
Can Menopause Lead to Cancer?
Menopause itself doesn’t cause cancer. So, risk of cancer after menopause is predominantly due to aging.
Oestrogen, for instance, can fuel the growth of some breast cancers. Its levels drop significantly after menopause, affecting the breast tissue. Regular screenings and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help early detection and prevention.
If you have concerns about menopause and cancer risk, consult a specialist for personalized guidance tailored to your situation.
Wondering about the prevalence of post-menopausal breast cancer? Let’s dive in.
How Common Is Breast Cancer After Menopause?

Breast cancer after menopause is more common than you might think. The estimated risk of developing breast cancer in women ages 50 to 60 is one in 43, and one in 29 in women ages 60 to 70. In women ages 70 and older, the risk is one in 26.
Unfortunately, this phase of life, often associated with newfound freedoms, increases risk for many.
Keep in mind that these stats aren’t meant to scare you. Instead, they’re here to empower. Understanding the prevalence empowers you to take charge of your health.
Regular screenings and staying vigilant about changes in your body can make a difference. Remember, knowledge is your best ally in this journey. We’re here to guide you through it.
Schedule regular screenings for early detection. Your health matters.
Let’s explore the factors contributing to breast cancer after menopause.
What Causes Breast Cancer After Menopause?

- Hormonal Replacement therapy (HRT):
Many post-menopausal women take hormone replacement therapy to overcome symptoms associated with menopause. If these pills contain high estrogen levels, this is a potential precursor to breast cancer.
- Age Factor:
With age, the risk of breast cancer increases. Hence, post-menopausal women are more susceptible.
- Genetic Influences:
Inherited mutations in BRCA genes can elevate the risk. This emphasizes the importance of understanding family history.
- Lifestyle Choices:
Unhealthy lifestyle habits can contribute to breast cancer risks. These include excessive alcohol consumption and lack of physical activity.
- Body Weight:
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial. This is because obesity is linked to an elevated risk of breast cancer.
- Previous Cancer History:
A history of breast or other cancers may heighten the risk. This necessitates vigilant monitoring.
- Radiation Exposure:
Past exposure to chest radiation, especially during childhood or early adulthood, can contribute to breast cancer risk in later life.
Understanding these factors empowers you to make informed choices. It enhances your proactive approach towards breast health after menopause.
What are the treatment options for menopausal breast cancer? Let’s find out.
Treatment for Breast Cancer After Menopause
1. Surgical Options:
When tackling post menopausal breast cancer, surgery often takes the lead. It’s the go-to for removing the tumor. There are times when chemotherapy is given before surgery, when it is called neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT).
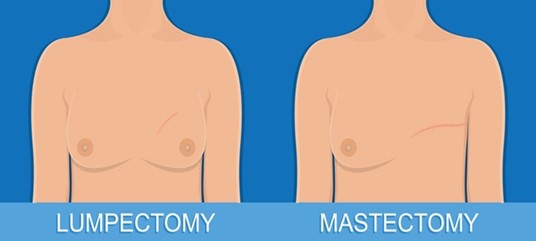
Lumpectomy and Mastectomy:
· A lumpectomy involves removing the tumor. In contrast, a mastectomy entails complete breast removal.
· Lumpectomy preserves breast tissue preserving the appearance.
- The risk of cancer coming back after mastectomy or lumpectomy is similar. So, choice depends on the patient.
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy:
· This minimally invasive procedure determines if cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes in the armpit.
· It helps plan further treatment and assess the extent of cancer spread.
2. Hormone Therapy:
· Women with hormone receptor-positive cancer may benefit from hormone therapy.
· It includes medications group called aromatase inhibitors. They target hormones that fuel the growth of certain breast cancers.
3. Chemotherapy:
· Chemotherapy may be advised to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors before surgery or after surgery. Chemotherapy works on the entire body.
· Side effects are temporary but can include hair loss, fatigue, and nausea.
4. Radiation Therapy:
· After surgery, radiation further reduces the risk of local recurrence.
· With modern radiation machines it’s a targeted approach, minimizing damage to healthy tissue.
5. Targeted Therapies:
· Targeted drugs like Herceptin focus on specific molecules promoting cancer growth and are used for HER2-positive breast cancers.
6. Immunotherapy:
· Uses the immune system to fight cancer cells.
· Still being studied but shows promising results for some breast cancers.
7. Follow-Up Care:
· Regular check-ups and imaging tests monitor recovery and detect any recurrence.
· Vital for long-term well-being and peace of mind.
8. Individualized Approach:
· Treatment plans are tailored to each patient.
· Discuss options thoroughly with your medical team for informed decisions.
Looking for personalized treatment options? Consult experts.
Uncover potential side effects associated with post menopausal breast cancer treatments.
Risks or Side Effects of Breast Cancer Treatments

Let’s uncover the risks and side effects of breast cancer treatments:
1. Surgery:
- Potential bleeding and infection
- Changes in breast appearance or sensation
- Lymphedema (swelling) in the arm especially after axillary lymph node dissection
2. Radiation Therapy:
- Skin changes (redness, irritation)
- Fatigue
- Rare risk of heart and lung issues for left-sided breast cancer
3. Chemotherapy:
- Temporary hair loss
- Nausea and vomiting
- Increased risk of infection
4. Hormone Therapy:
Increased risk of osteoporosis is seen with aromatase inhibitors.
5. Targeted Therapy:
- heart failure that is reversible.
- Skin reactions at the injection site
- Liver problems (in some cases)
- GI issues like diarrhoea
- Remember, everyone’s response varies. Contact your healthcare team to manage and minimize these effects. They’ll ensure a smoother journey through your breast cancer treatment.
Need support during treatment? Connect with our support services for personalized assistance.
Let’s discuss preventive strategies for post menopausal breast cancer.
How Can I Prevent Breast Cancer After Menopause?
- Stay Active: Regular exercise can lower your breast cancer risk post-menopause. This includes activities like brisk walking or cycling.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Strive for a balanced weight. This is because obesity increases the risk of breast cancer.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: Cut down on alcohol. Even small reductions can make a significant impact on your risk.
- Healthy Diet Choices: Opt for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These power-packed foods contribute to overall well-being.
- Regular Check-ups: Schedule routine check-ups and mammograms. Early detection is critical for effective management.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) Awareness: If considering HRT, discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor. It is not one-size-fits-all.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a risk factor for many cancers, including breast cancer. Quitting is a significant step towards prevention.
- Sunshine Vitamin: Ensure you’re getting enough Vitamin D, either through sunlight or supplements. It plays a protective role.
Remember, small lifestyle adjustments can create a significant shield against menopause breast cancer. Stay proactive and prioritize your well-being!
Conclusion
Facing breast cancer after menopause can be overwhelming. But remember, you’re not alone in this journey. With the guidance of experts like Dr. Sandeep Nayak, a reputable oncologist in India, you can navigate the complexities of menopause breast cancer. Knowledge is key. By staying informed about risk factors, tailored treatments, and potential outcomes, you empower yourself to make informed decisions.
Seeking further guidance? Book an appointment for personalized advice.
Unveil FAQs about breast cancer after menopause. Let’s get your questions answered.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Is breast cancer less aggressive after menopause?
After menopause, breast cancer can exhibit varying aggressiveness. Some tumors may be less aggressive. Yet, it is crucial to remain vigilant with regular screenings. It helps in early detection and effective management.
2. Can menopause cause a breast lump?
Menopause itself doesn’t directly cause breast lumps. But, hormonal changes during this phase may lead to benign conditions. Any new lump should be promptly evaluated to rule out any concerns.
3. What are the key signs of breast cancer after menopause?
Watch for changes like lumps, skin changes, or nipple discharge. Regular self-checks and mammograms are crucial for early detection.
4. How often should I get a mammogram after menopause?
The frequency of mammograms depends on your health history and risk factors. Generally, women are advised to have mammograms every 1-2 years. Your healthcare provider can provide personalized recommendations.
5. Can stress impact breast cancer risk after menopause?
Stress alone may not directly cause breast cancer. Yet, managing stress is crucial for overall health. Adopting stress-reducing practices contributes to your well-being.

