The liver is one of the body’s biggest and most crucial organs. It is essential for digestion, metabolism, and detoxification. Unfortunately, the liver can be affected by several illnesses, including liver tumors, just like any other organ. Many people find liver tumors a scary reality filled with dread, anxiety, and confusion.
“The liver is a crucial organ for maintaining the health of our body, so if anything goes wrong, it can be devastating,” says Dr. Sandeep Nayak, a renowned Surgical Oncologist in India.

Having queries and worries about a vital organ like the liver is normal. So read on if you have a liver tumor, know someone who does, or want to learn more. This blog will explore the various types of liver tumors, their signs and symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
About Liver tumor
 A liver tumor, also called a hepatic tumor, is an abnormal growth or aggregation of cells in the liver. It could originate from the liver cells or tissues and be benign or malignant. Liver tumors can develop for a number of reasons, such as infection, chronic liver disease, and toxin exposure.
A liver tumor, also called a hepatic tumor, is an abnormal growth or aggregation of cells in the liver. It could originate from the liver cells or tissues and be benign or malignant. Liver tumors can develop for a number of reasons, such as infection, chronic liver disease, and toxin exposure.
While some liver tumors may not show symptoms, others might be painful or uncomfortable. The tumor’s size and location may affect liver function and general health. Monitoring liver health through regular checkups and keeping a healthy lifestyle is crucial to lowering the risk of developing liver tumors.
“Regular visits to a medical professional can help detect the onset of a liver condition and treat it before it progresses into a full-fledged liver cancer,” advises laparoscopic surgeon Dr. Sandeep Nayak.
Difference between Liver tumor & Liver cancer
A liver tumor is any abnormal growth or cell mass that forms in the liver. It can be benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Benign tumors are typically not life-threatening and can be removed surgically. Malignant tumors can spread to other body regions and need immediate treatment.
Hepatic cancer, another name for liver cancer tumor, refers specifically to a malignant tumor that develops in the liver. The cancerous condition begins in the liver’s cells and can potentially spread to other organs. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most prevalent type of liver cancer out of several others.
“A liver tumor is a general term that refers to any abnormal growth in the liver,” explains robotic cancer surgeon Dr. Sandeep Nayak, “while liver cancer specifically refers to a malignant tumor that originates in the liver.”
Let us take a look at the common types of liver tumors.
Different types of liver tumors
Hemangioma:
The most common benign liver tumor, it is made of blood vessels and is usually tiny and symptomless.
Hepatocellular adenoma:
A benign liver tumor more frequently found in women can become huge and cause pain or other symptoms. It is commonly linked to the use of oral contraceptives.
Focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH):
Usually a tiny and asymptomatic non cancerous liver tumor, it comprises healthy liver cells organized abnormally.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC):
The most common malignant tumor of liver, which starts in liver cells and can spread to other body organs.
Cholangiocarcinoma:
Less frequent than HCC, cholangiocarcinoma is a form of liver cancer that develops in the cells lining the bile ducts. It can be aggressive and challenging to cure.
Angiosarcoma:
An uncommon type of liver cancer arising in the cells lining the blood vessels in the liver, often due to exposure to certain chemicals or radiation.
Metastatic liver cancer:
The most prevalent type of liver cancer in adults, it is cancer that has progressed from another organ, such as the colon, breast, or lung, to the liver.
While the root cause of each type of liver tumor can differ, a number of common factors can raise the chance of developing liver tumors.
Causes and risk factors for liver tumors
Listed below are some common causes and risk factors for liver tumors:
Chronic liver disease:
Liver tumors can be more likely to form in people with chronic liver disease, such as cirrhosis, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), or hepatitis B or C.
Environmental factors:
Exposure to chemicals or poisons can raise the risk of developing liver tumors. Examples of such chemicals include vinyl chloride, arsenic, and aflatoxins, produced by a particular form of mold.
Lifestyle factors:
Heavy drinking, smoking, and obesity increase the chance of developing liver tumors.
Family history:
Liver tumours are more likely to occur in those with a family history of them or with certain genetic disorders such as hereditary hemochromatosis.
Age and gender:
Older persons and men are more likely to develop liver tumours.
Diabetes:
Liver tumours are more likely to form in people with diabetes.
Metabolic disorders:
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency and Wilson’s disease are two examples of metabolic abnormalities that can raise the chance of developing liver tumors.
“Having one or more of these risk factors does not guarantee a person will develop a liver tumor,” says oncological surgeon Dr. Sandeep Nayak. “Liver tumors can also occur in persons who do not have any known risk factors.”
Let us look at the symptoms and diagnostic tests to detect liver tumors.
Symptoms of liver tumor

- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Swelling or enlargement of the abdomen
- Loss of appetite or weight loss
- Nausea or vomiting
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Fatigue or weakness
- Pale or clay-colored stools
- Dark urine
If you experience any of the above symptoms, please consult Dr. Sandeep Nayak to assess your condition and run some essential diagnostic tests.
Diagnostic tests for liver tumor include:

Blood tests may be done to check liver function, including liver enzyme levels and tumor markers.
Imaging tests:
Imaging tests such as liver tumor ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, or PET scan can detect liver tumors and determine their size, location, and spread.
Biopsy:
A small sample of liver tissue may be examined under a microscope to determine if it is cancerous or benign.
Angiography:
A dye is injected into an artery in the liver to help visualize blood vessels and detect abnormalities.
Laparoscopy:
A tiny camera is inserted through a small incision in the abdomen to allow the doctor to see the liver and any tumors up close.
Endoscopy:
A thin, flexible tube with a camera on the end is passed down the throat and into the stomach to examine the liver and bile ducts.
Not all liver tumors cause symptoms; some may be detected incidentally during routine medical tests or exams.
“You must not ignore any discomfort or abnormalities in your body or sensations,” cautions cancer specialist Dr. Sandeep Nayak. “Early detection makes it possible to look at the best possible liver tumor treatment options for optimum results.”
Liver tumor treatment
Oncological surgeon Dr. Sandeep Nayak performs the following procedures frequently for liver Cancer Treatment in Bangalore.
The treatment choices for liver tumors depend on the size and location, the stage of the malignancy, and the patient’s overall health.
- Surgery:
Liver tumor surgery is frequently used if the tumor is confined and can be removed safely without harming healthy liver tissue. The most common liver surgery to remove tumor is hepatectomy, which involves removing a part of the liver.
- Liver transplant:
On occasion, a liver transplant may be necessary if the tumor is too large or located in a location that cannot be removed surgically. Only patients who meet specific criteria and can access a suitable donor liver are eligible to employ this approach.
- Radiation:
High-energy radiation is used to eliminate cancer cells. The delivery is possible internally directly to the liver (brachytherapy) or externally (external beam radiation).
- Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy uses drugs, administered orally or intravenously, to eradicate cancer cells from the liver and other body parts.
- Targeted therapy:
Drugs used in targeted therapy directly target cancer cells and stop their division and growth. They may be utilized separately or in conjunction with other treatments.
- Ablation therapy:
This technique applies heat or cold to kill liver tumors. The medical professional can administer this through a tiny skin incision or a needle into the liver.
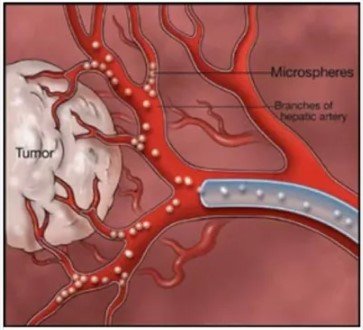
- Embolization:
In embolization, the tumor’s blood supply is cut off, resulting in tumor death or shrinkage. Numerous methods can achieve this, such as obstructing blood vessels with microspheres (tiny beads or coils).
If you or a loved one has a liver condition, please visit cancer specialist Dr. Sandeep Nayak. Dr. Nayak frequently collaborates with his team of experienced oncologists to diagnose the condition’s specifics and determine the best course of treatment.
Conclusion
A liver tumor diagnosis can be emotionally difficult for patients and their loved ones. However, the outcomes for individuals who receive therapy have significantly improved due to developments in medical science and technology.
Patients can conquer this challenge and emerge even stronger with the assistance of knowledgeable healthcare experts and a helpful network of family and friends. We can continue to be optimistic about managing liver tumors as medical professionals work to discover new therapies and cures for benign and malignant liver tumors.
If you seek a reliable treatment for your liver condition, please get in touch with Dr. Sandeep Nayak, often deemed the best oncologist in India.
Together, we can fight against this ailment and improve life for those impacted.